Life's a beach: finding trends in marine debris across Australia
Ten years of citizen science data has informed a ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou study which found plastic dominates the rubbish found on Australian beaches.
Ten years of citizen science data has informed a ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou study which found plastic dominates the rubbish found on Australian beaches.

Plastic is 84 per cent of all rubbish found across Australian beaches, a ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou-led study based on one of the largest marine debris databases in the Southern Hemisphere has found.
More than 2000 organisations and 150,000 citizen scientists have participated in the Australian Marine Debris Initiative [AMDI] by sorting and tallying up marine debris they have collected since it was set up by the not-for-profit Tangaroa Blue Foundation in 2004.
Now a study led by ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou Science has filtered and analysed 10 years of the AMDI Database and created a national map of patterns in marine debris.
The study found that almost half of all debris could be related to land-based sources (litter and dumping on land)ô and 7 per cent to dumping at sea.
But 42 per cent of debris could not be related definitively to a source due to the debris breaking down into smaller fragments, which the researchers say highlights the legacy of plastic left in our environment, continually fragmenting into smaller pieces until it is microplastics.
The findings have been published in .

Jordan Gacutan is a PhD candidate in ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou Science's Centre for Marine Science and Innovation.
ãThe AMDI Database contains entries of beach clean-ups across Australia, but the added value of this database is that volunteers take the time to categorise what they find, sorting and counting the amounts of plastic, glass, rubber, metal, paper and other items,ã study lead author and PhD candidate, Jordan Gacutan from ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou Scienceãs Centre for Marine Science and Innovation in the School of Biological, Earth and Environmental Sciences, says.
ãWe can combine this rich data over space and time to get patterns of the marine debris and plastic problem across Australia.
ãThis study shows, with unprecedented resolution, the variation in debris items both regionally and across Australia.ã
Study co-author and Dean of ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou Science, Professor Emma Johnston, says very few environmental stresses are able to be measured on a national scale.
ãSo the 150,000 citizen scientists who have contributed to this database are doing an amazing favour for Australia,ã Prof. Johnston says.
ãTheir passion for the environment gives us one of the few continental-scale insights into the global marine problem.ã
For the AMDI Database, the Tangaroa Blue Foundation developed a method of categorising and counting all the rubbish collected by a range of citizen scientists and partner organisations, from families to government campaigns.
ãWe designed the methodology, host it and manage the database, but the data is owned by 150,000 people whoô have contributed to that database,ã study co-author and Tangaroa Blue Foundation founder and chief executive officer Heidi Tait says.
ãThis is the impact of working together and the results really highlight that one intervention isnãt going to solve the plastics in our oceans issue, and one sector or one stakeholder group is not going to be able to solve it on their own, either.
ãWe need to collaborate and this network is a perfect example of partners who have achieved something quite monumental.ã
The AMDI Database now has almost 20 million entries, but the ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou study focused on the 10-year period from when the database registered beach clean-ups at a national level.
Ms Tait says the AMDI Database showed there was a very different marine debris signature at a regional scale.
ãThe data shows that what we find in Cape York is completely different to what we find in Port Phillip Bay in Melbourne,ã she says.
The ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou study looked at the national picture, but also grouped its findings according to the six ãbioregionsã the Australian government uses to manage our oceans and coasts.
These are: North (Northern Territory to Cape York), North-west (WA); South-west (lower WA and SA); South-east (including Victoria and Tasmania) and Temperate east (mainly NSW) and Coral Sea/Great Barrier Reef Marine Park.
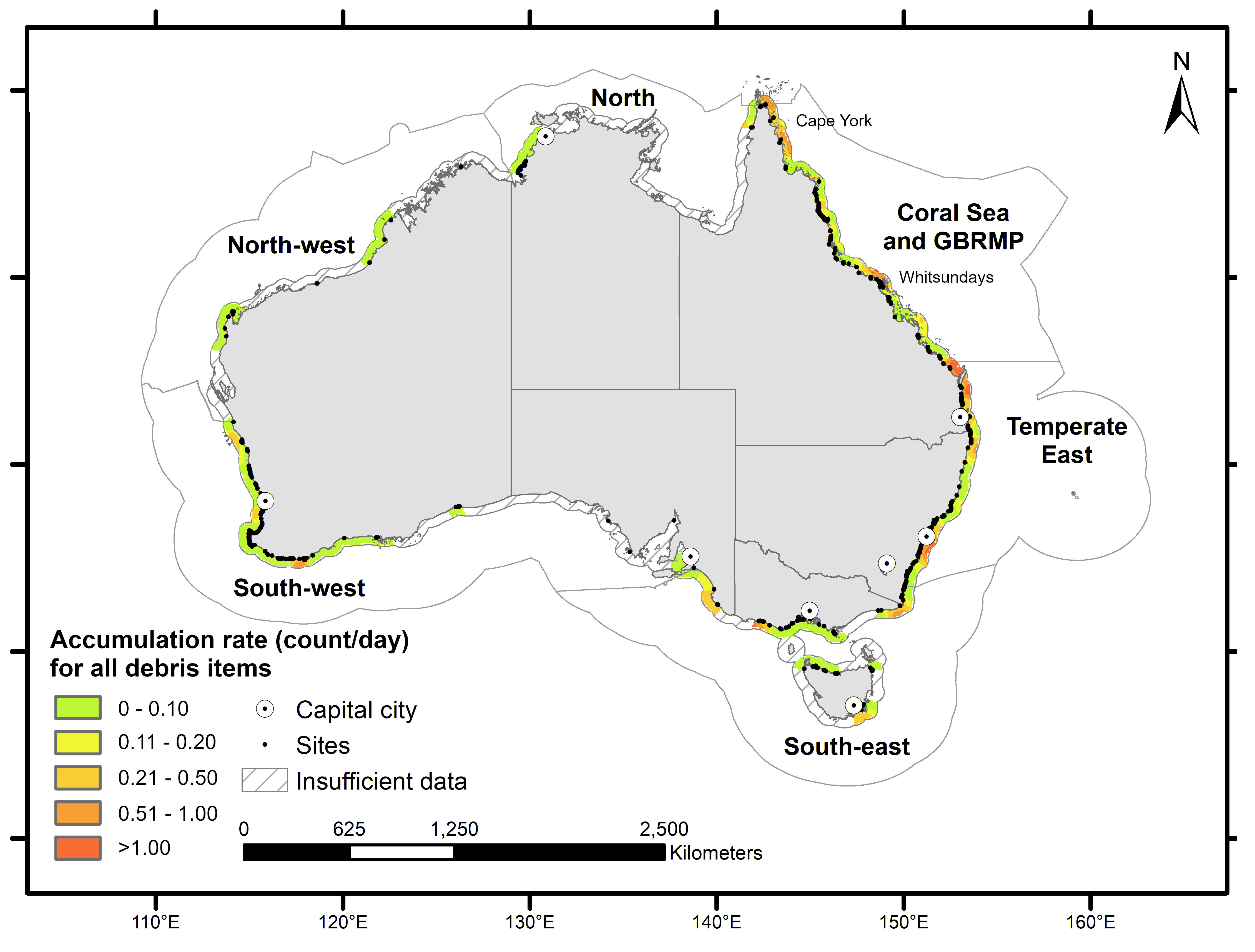
A map of the accumulated count [per day] of all debris averaged per clean-up site across the Australian coast. Coasts with insufficient sites were not considered in the analysis. Graphic: Jordan Gacutan
Mr Gacutan says that by looking at what items were found on beaches, we can better understand the problem items and where they came from.
ãSome bioregions have a high amount of fishing debris, such as fishing floats and nets, while others have a bigger problem with littering, and you can identify these patterns through what items you find on these coastal clean-ups,ã he says.
The South-east and South-west regions have higher amounts of fishing items but, on the other hand, the Temperate East had three times the proportion of cigarette butts, compared to the national average, which shows a problem with local litter, the study suggested.
The study found about 40 per cent of all marine debris across Australia was from littering, particularly near capital cities where a lot of plastic ends up on the beach from stormwater drains.
ãOn the other hand, although Cape York in Queensland had a huge amount of debris, most of it came from external sources, for example, floats and plastic bottles that might have been dumped both at sea or floated from other countries," Mr Gacutan says.
ãWe know that Cape York is very, very remote so the amount of plastic weãre finding on beaches isnãt contributed by the people living there."
Ms Tait says that better evidence needs to be used to inform how we manage the growing marine debris problem.
ãWe need to be really targeted and strategic in what changes are put in place to mitigate marine debris, and we need to measure and monitor to make sure we are actually solving the problem, thatãs where the data is going to be so critical moving forward,ã she says.
Dr Graeme Clark, senior author of the study and Senior Research Associate at ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou, says the study focused on filtering the data to make sure that it was as accurate and reliable as possible before it was used.
ãOne of the main concerns that people have with citizen science data is the quality, accuracy and reliability of the data that weãre getting from these clean-ups,ã he says.
ãYou do get a huge variability in the quality, for example, some people might start cleaning the grassed area at a beach, or the car park; children collect differently from adults; and this really limits comparisons between sites.
ãWe tried to maximise the quality of the data and control the sites that we looked at by really conservative filtering.
ãWe only looked at sites that were sandy, ocean facing, and werenãt modified by structures like seawalls and breakwaters.ã

Examples of marine debris collected by citizen scientists on Australian beaches as part of the Australian Marine Debris Initiative. Photos: Tangaroa Blue Foundation.
Dr Clark says that the methods presented by the ôÕÑ¿èÓmadou team could impact how citizen science databases are used and improve how marine debris data is collected globally.
ãImproving the quality and rigour of citizen science data makes it easier to use in management and decision making,ã he says.
ãCitizen science datasets are powerful tools for marine debris monitoring and can help shape management plans to better tackle the problem of marine debris and plastic pollution at a localised level.ã
Ms Tait says the most unique aspect of the AMDI Database is that itãs based on a scalable model which identifies the source of the debris.
ãIf you look at whatãs currently happening internationally with discussions around global treaties on plastic, nationally with the National Plastics Plan, and state government plans to address single-use plastics: how are we going to measure those to make sure that those policies are having impact?ã she says.
ãFor example, if a Global Treaty on Plastics is formalised through the United Nations, we should see the 95 per cent of international marine debris we find in Cape York decrease in the future, if this treaty is successful.
ãThis is a way to measure the impact of mitigation strategies that are put in place to see whether theyãre actually making a positive impact and reducing marine debris and litter at the source.ã
Read the .